It is important to be aware that germs can cause infections. Some of the most common infections are caused by viruses, such as the common cold and the flu. Bacteria can also cause infections, such as pneumonia and strep throat. Germs can also cause infections in the skin, such as impetigo and boils, which is why it’s so important to prevent the spread of infection. Keep reading to learn about the top germs that cause infection.
Staphylococcus Aureus
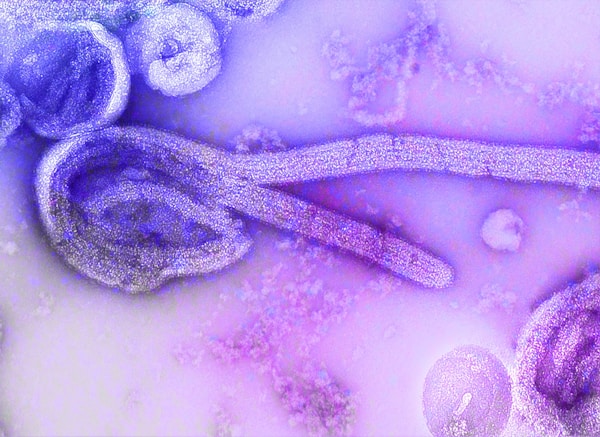
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that is commonly found on the skin and in the nose. It can cause a variety of infections, including skin infections, pneumonia, and bloodstream infections. S. aureus is one of the most common causes of skin infections, and it can cause a wide range of symptoms, from a simple boil to a life-threatening infection. S. aureus can also cause serious illnesses, including pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and meningitis. In addition, S. aureus can also cause food poisoning.
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive bacterium that is responsible for a wide variety of diseases, including breathing infections, meningitis, and sepsis. It is a common cause of respiratory tract infections and is the leading cause of death from bacterial infections in the United States. S. pneumoniae is spread through contact with respiratory secretions and is most commonly acquired from close contact with other people, such as in schools, daycare centers, and nursing homes. It is also found in the environment and can be acquired from contact with contaminated water or soil. S. pneumoniae is a highly contagious organism and can cause serious illness in healthy people as well as those who are immunocompromised.
Escherichia Coli
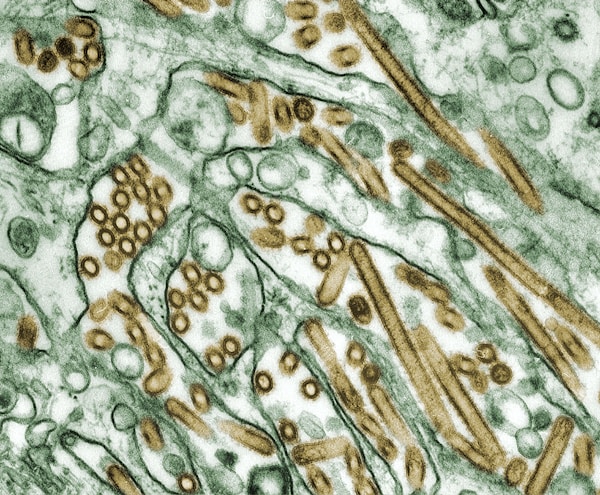
Escherichia coli, commonly referred to as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It is a facultative anaerobe and usually inhabits the lower intestine of warm-blooded animals. E. coli is a facultative anaerobe because it can survive in the presence or absence of oxygen. There are many strains of E. coli, and some are pathogenic, meaning they can cause disease in humans. The most common pathogenic strains of E. coli are enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC), and enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC). These strains are associated with diarrhea, often bloody diarrhea, in humans.
E. coli is also a common cause of food poisoning. The most common food sources of E. coli are undercooked ground beef, unpasteurized milk and juice, and contaminated water. Symptoms of food poisoning caused by E. coli include nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. E. coli can also cause other types of infection, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and sepsis.
Haemophilus Influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae is a Gram-negative, aerobic, pleomorphic, coccobacillus bacterium. It is a member of the Pasteurellaceae family. H. influenzae is a facultative anaerobe and can grow on both blood agar and chocolate agar. It is oxidase-positive and catalase-positive. H. influenzae is a pathogen that can cause a wide range of diseases in humans, including respiratory infections, meningitis, and bacteremia. It is most commonly spread through the air and can be easily transmitted from person to person. H. influenzae is also a common cause of ear infections in children. H. influenzae is treated with antibiotics, such as ampicillin, doxycycline, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
Overall, the top germs that cause infection are very important to be aware of. They can cause a variety of illnesses, some of which can be quite serious. It is important to take steps to protect yourself from these germs and promote the control of infections, such as washing your hands regularly and staying up-to-date on vaccinations.




